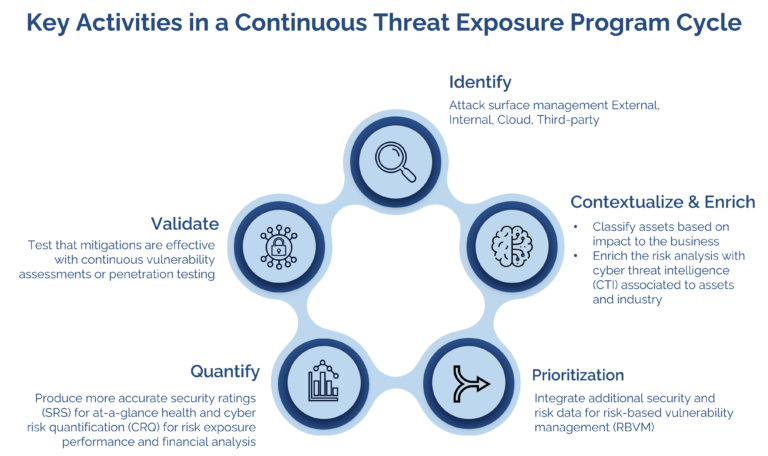
Continuous Threat Exposure Management – The 6 Aspects You’ll Need to Address Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is an…
"This is an excellent starting point for any organization that wants to get serious about their cyber risk management. The system has the capability to grow as you become more sophisticated in your use"
IT Director
Services Industry
In cybersecurity, a model known as the “5C” emerges as a crucial framework. This article discusses and explains the 5 C’s of cybersecurity—Change, Continuity, Cost, Compliance, and Coverage—highlighting their importance in modern-day digital defense mechanisms.
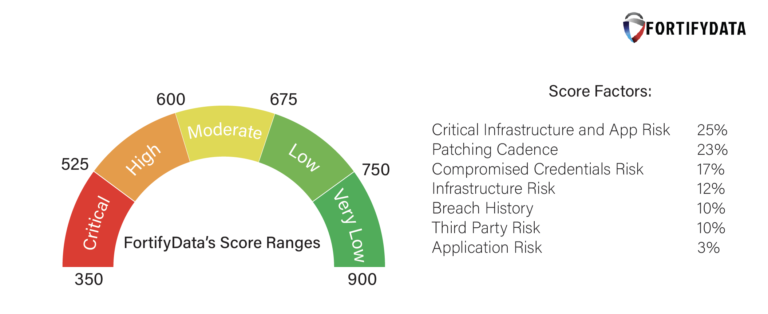
The digital landscape is an ever-evolving realm where securing assets against threats has become paramount. A term closely related to this endeavor is security ratings, a pivotal aspect in comprehending an organization’s overall security posture. The cyber security rating scale further provides a nuanced insight into various aspects contributing to a secure digital setup.
The 5 C’s of cybersecurity offer a structured approach towards understanding and implementing a robust cybersecurity framework. Here’s a closer look at each of these pillars:
Additional Resources
Cybersecurity rating scale explained
What are security ratings used for?
How are security ratings created?
What is a good cybersecurity rating?
How do you improve your security rating?
Is it easy to switch security ratings providers?
Why is my security rating wrong?
What Kind of Company is BitSight?
What is the Highest Security Rating?
What is the difference between SecurityScorecard and BitSight?
The Evolution of Cybersecurity Ratings and How They Can Boost Risk Visibility

Cybersecurity encompasses various domains, each aimed at safeguarding different facets of an organization’s digital presence. These include Network Security, Information Security, Endpoint Security, Application Security, and Cloud Security. Each type utilizes a range of cyber security tools like firewalls, anti-malware software, and encryption tools to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of digital assets. Some or all of these components can be included as risk factors that are weighed in a cyber security rating scale by a security ratings provider. Understanding these types provides a foundational knowledge towards establishing a robust cybersecurity framework.
A well-rounded cybersecurity framework includes five essential functions from the NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Identification, Protection, Detection, Response, and Recovery. Coupled with the types of cyber security, these functions form a robust defense mechanism for the domains of enterprise IT for cybersecurity – Network security, Information Security, Endpoint Security, Application Security and Cloud Security. Real-world cyber security examples like incident response plans and regular security audits help in understanding how these elements intertwine to bolster an organization’s resilience against cyber threats, thereby promoting a culture of security awareness and preparedness.

There are a few ‘3 Cs of Cyber Security depending on what you are trying to convey:
3 C’s of cyber security investigative analysis – Context, Correlation and Causation
3 C’s of Cybersecurity Prevention – Comprehensive, Consolidated and Collaborative
3 C’s of Cybersecurity Awareness – Communication, Collaboration, Culture

Understanding the 5 C’s of cybersecurity—Change, Continuity, Cost, Compliance, and Coverage—provides a structured approach towards building a robust cybersecurity framework. Alongside, exploring other models and concepts like the security ratings and cyber security rating scale can offer a more rounded understanding, aiding organizations in navigating the complex cybersecurity landscape effectively. Through a concerted effort in implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures, organizations can significantly mitigate risks, ensuring a safer digital environment for their operations.
Additionally, leveraging automation for cybersecurity processes and assessments like FortifyData provides can significantly bolster an organization’s cybersecurity measures.
Discover how FortifyData can revolutionize your cybersecurity strategy. Get a Free Cyber Risk Assessment to discover current cybersecurity risks within your organization, and find actionable information to improve your security posture.


| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |