
4 Steps to Attack Surface Management Businesses face a wide range of cyber threats that can compromise their sensitive…
"This is an excellent starting point for any organization that wants to get serious about their cyber risk management. The system has the capability to grow as you become more sophisticated in your use"
IT Director
Services Industry
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is an approach to cyber risk management that is gaining popularity as it presents a comprehensive and cyclical program for identifying and mitigating cyber risks.
Many organizations already have a component or two of CTEM program in place, though achieved with different point-solutions that are challenged with data interoperability issues that hinder analysis and workflow automation. Implementing a CTEM program at an organization benefits multiple departments by informing and directing actions and provides the opportunity for tool consolidation that enables a quicker analysis and response to the underlying cyber risk data.
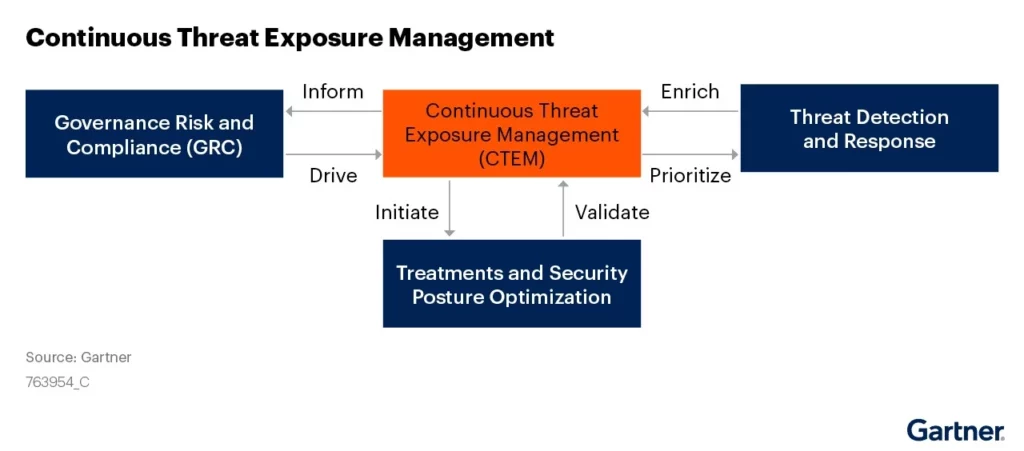
CTEM is an ongoing process that involves continuously identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential security threats. It enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities in their systems and networks and communicate next steps to prevent or minimize the impact of attacks. According to Gartner® who recently published the report “Implement a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) Program”
“Enterprises fail at reducing their exposure to threats through self-assessment of risks because of unrealistic, siloed and tool-centric approaches. Security and risk management leaders must initiate and mature a continuous threat exposure management program to stay ahead of threats. “Gartner noted that “organizations prioritizing their security investments based on a continuous exposure management program will be three times less likely to suffer from a breach. At any stage of maturity, a CTEM cycle must include five steps to be completed: scoping, discovery, prioritization, validation and mobilization.”

We see the CTEM cyclical program built on a foundation of familiar processes enabled through integrated technologies or integrated capabilities within a unified cyber risk management platform.
Organizations that implement a CTEM process will realize a few key benefits:
Tool consolidation.
According to Gartner (“Continuous Threat Exposure Management: An Emerging Security and Risk Management Category”, June 2021.) “Consolidation of tooling is essential to success with CTEM, since a high degree of integration and automation is required to ensure proper risk reduction.” CTEM integrates multiple security tools and technologies, allowing organizations to identify and respond to threats more efficiently. This consolidation enables security teams to reduce the complexity of their security stack, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
Continuous monitoring of security posture.
Another benefit of CTEM is its ability to provide continuous monitoring and visibility into an organization’s security posture for proactive prevention. Traditional security approaches are often reactive, with teams waiting for alerts before responding to threats or focused on an ‘assumed breach’ mentality and hunting for signals. CTEM, on the other hand, provides continuous monitoring and real-time visibility into an organization’s security posture, enabling teams to proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
Streamline incident response.
CTEM also helps organizations to streamline incident response processes. By continuously monitoring for threats and vulnerabilities and communicating shared data across departments, organizations can develop and implement response plans before an incident occurs. This CTEM process can help minimize entry points and the preparation helps to minimize the impact of an attack, reduces downtime, and accelerates recovery time.
As mentioned, proper tool selection and integration is a foundational component to enabling a threat exposure management approach, incorporating automation, and adopting continuous processes.
Organizations need to select appropriate security tools that can integrate with each other and provide comprehensive coverage. Gartner (“Implement a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) Program”, July 2022.) suggests the following tools in a CTEM program:
FortifyData’s platform provides many of the capabilities that a CTEM program should have. The FortifyData platform enables Enterprises to get a unified view of cyber risk that affects the organization with the ability manage cyber risk by subsidiaries or departments. The FortifyData platform combines automated attack surface assessments with asset classification, risk-based vulnerability management, security ratings and third-party risk management, to provide an integrated view of cyber risk. This helps organizations with tool consolidation, leveraging one data source that is interoperable and provides continuous threat exposure management.
Gartner noted that “organizations prioritizing their security investments based on a continuous exposure management program will be three times less likely to suffer from a breach.” If you’re ready to get a jump-start on implementing your CTEM program, schedule a demo from FortifyData.



| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |