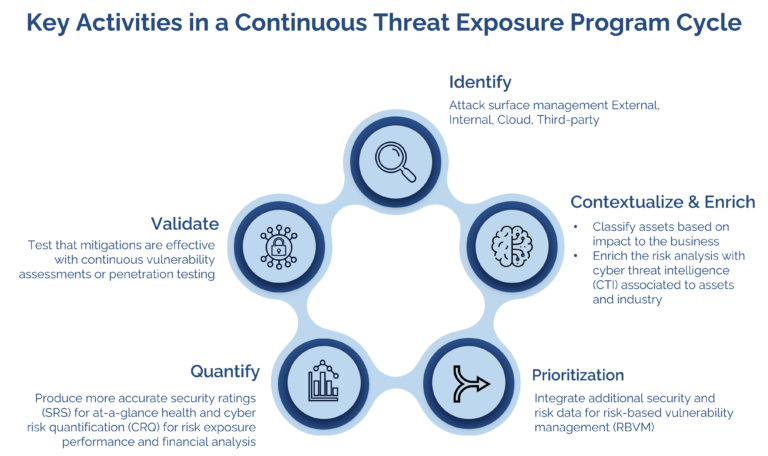
Continuous Threat Exposure Management – The 6 Aspects You’ll Need to Address Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is an…
"This is an excellent starting point for any organization that wants to get serious about their cyber risk management. The system has the capability to grow as you become more sophisticated in your use"
IT Director
Services Industry
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding various security ratings is crucial for organizations to manage and mitigate risks effectively as a metric that indicates low to high cybersecurity risk.
Among the many frameworks available, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has a rating scale that provides a structured approach to evaluating cybersecurity risk and maturity. Many of the leading vendors leverage some components of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework built into their automation of cyber risk analysis that helps calculate the security rating.
Through this lens, the cyber security rating scale broaden the horizon of how organizations can protect their assets and data. The term NIST risk rating table is often mentioned in discussions surrounding this topic, underscoring its importance in the cybersecurity domain.
The NIST rating scale is a part of the NIST’s broader framework for managing cybersecurity risks. This scale assists organizations in understanding, managing, and communicating about cybersecurity risks, making the NIST risk rating table a crucial tool for any cybersecurity initiative.
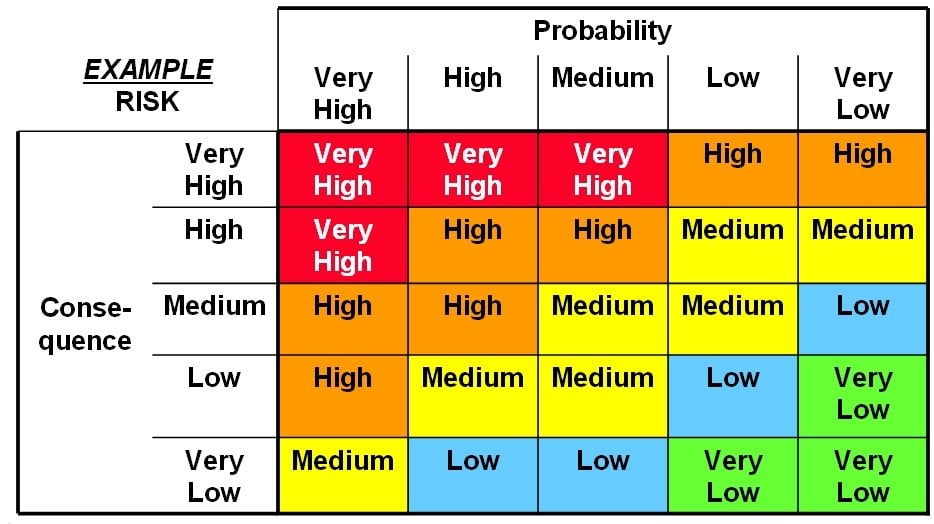
NIST Risk Assessment Matrix / NIST Risk Rating Table
Additional Resources
Cybersecurity rating scale explained
What are security ratings used for?
How are security ratings created?
What is a good cybersecurity rating?
How do you improve your security rating?
Is it easy to switch security ratings providers?
Why is my security rating wrong?
What Kind of Company is BitSight?
What is the Highest Security Rating?
Select What are the 5 C’s of Cybersecurity?
What is the difference between SecurityScorecard and BitSight?
What is the difference between BitSight and RiskIQ?
What is the difference between SecurityScorecard and CyberGRX?
NIST’s framework is segmented into different implementation tiers to help organizations gauge their approach towards managing cybersecurity risks. Utilizing a NIST risk assessment template can aid in understanding where an organization stands in terms of its cybersecurity readiness. The NIST scoring methodology further breaks down the evaluation process, making it helpful for organizations to identify areas of improvement within the implementation tiers.
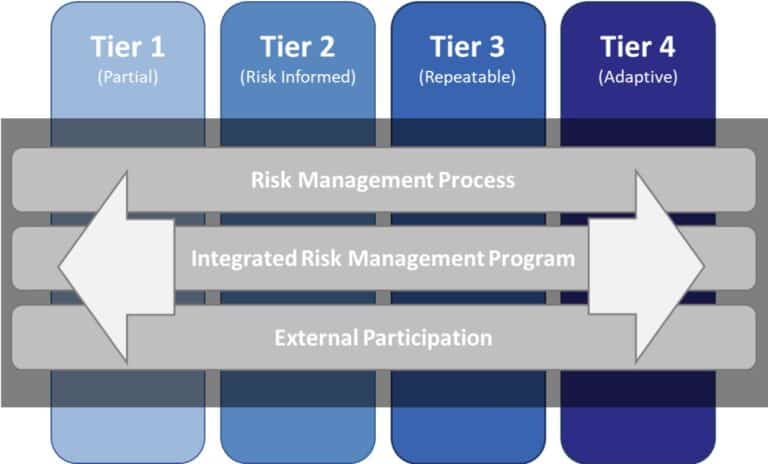
Image: NIST Framework Implementation Tiers, source: https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework/online-learning/cybersecurity-framework-components
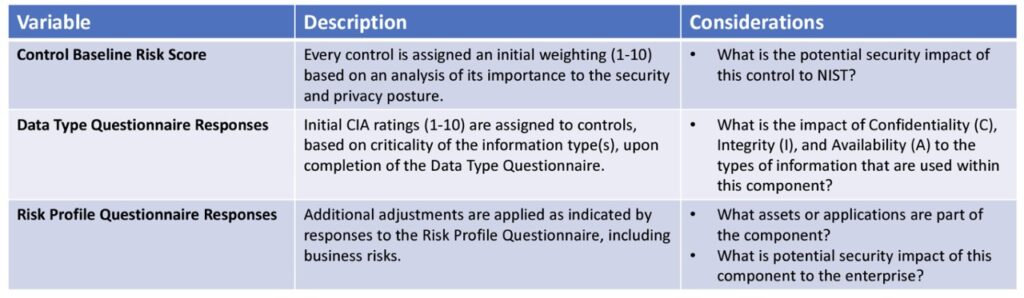
The process of evaluating cybersecurity risks within the NIST framework is termed as NIST cybersecurity risk scoring. This encompasses utilizing the NIST cybersecurity framework alongside a NIST risk assessment template to carry out a systematic assessment of cybersecurity risks faced by an organization. Scoring helps in prioritizing risks and allocating resources efficiently to address the most critical vulnerabilities. This provides an “integrated view of NIST risk posture across the enterprise with quantitative metrics across systems and components”
“Risk Scoring provides a foundation for quantitative risk-based analysis, assessment, and reporting of organizational IT assets. By applying ratings to controls and generating scores for components, stakeholders have a relative understanding of risk from one system compared to another. The variables that can affect a control’s potential risk score is outlined below.”
The 5 Levels of the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) framework is designed to provide a step-by-step approach to improving an organization’s cybersecurity posture against the 5 core categories of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework functions. By adhering to this structured approach, organizations can gradually enhance their cybersecurity measures, ensuring a secure and resilient operational environment. The NIST cybersecurity framework and NIST scoring methodology serve as the backbone for these levels, providing the necessary guidelines and assessment tools for progressing through the levels.
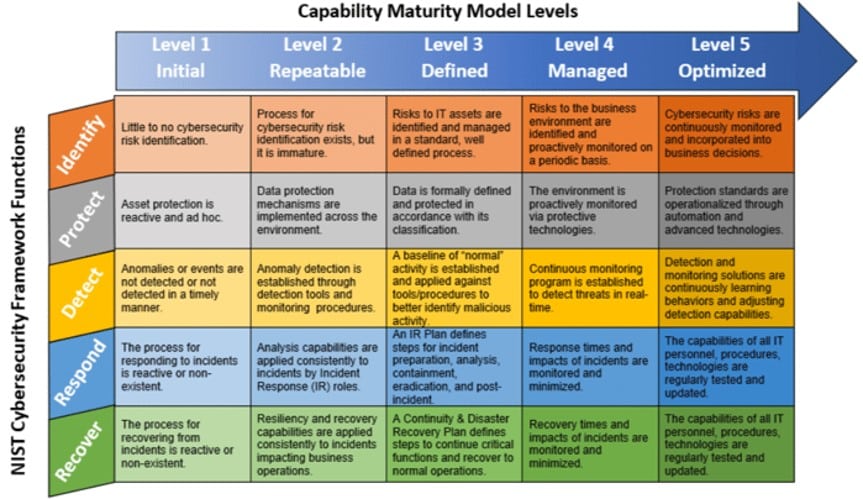
Source: Charles IT Blog
Here’s a closer look at each level:
Each level in the NIST framework serves as a milestone on the journey to achieving a strong cybersecurity posture. By understanding and working through these levels, organizations are better equipped to protect their assets and data against an ever-evolving array of cybersecurity threats.
Understanding the NIST rating scale and its various components is instrumental for organizations to fortify their cybersecurity posture. While this differs from the security rating and the cybersecurity rating scale those security rating services vendors have, many have elements of the NIST CSF built into their automated analysis of cyber risk that calculates the security rating.
The structured approach that NIST provides empowers organizations to tackle cybersecurity challenges head-on. As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, adapting a robust framework like NIST’s is a prudent step towards ensuring a secure operational environment. For further insights into enhancing your organization’s cybersecurity framework, explore our comprehensive guide on security ratings and how they play a pivotal role in today’s digital landscape.


| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |