
Penetration Testing vs Vulnerability Assessments: Understanding the Differences Penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are two important components of any…
"This is an excellent starting point for any organization that wants to get serious about their cyber risk management. The system has the capability to grow as you become more sophisticated in your use"
IT Director
Services Industry
Navigating the complex landscape of cyber threats requires constant vigilance and proactive measures. Implementing a cyber security risk assessment and conducting cyber threat assessments is fundamental to understanding your vulnerabilities, prioritizing risks, and taking control of your organization’s security posture. This in-depth guide provides a cyber security risk assessment checklist to navigate the process effectively.
A security assessment, often referred to as a security risk assessment or information security risk assessment, is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential threats and vulnerabilities within your IT infrastructure. Many companies follow the prescriptive outline these assessments take as a security risk assessment checklist. This comprehensive evaluation helps organizations understand their security posture through cyber threat assessments, prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact, and develop mitigation strategies to address them.
A cyber security risk assessment checklist serves as a roadmap for conducting a thorough security assessment. It outlines key areas to examine, potential vulnerabilities to identify, and essential questions to ask. Utilizing a pre-defined cyber security audit checklist pdf ensures a consistent and comprehensive evaluation, regardless of the assessor’s experience level.
One of the more common cybersecurity risk assessment checklists that companies use is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). This Framework provides a good baseline for any business in any industry to adhere to. Please note, companies within certain industries (Finance, Government, Healthcare) may have additional requirements to those found here- please consult those requirements to discover what is net new to this framework.
This checklist provides a structured approach to conducting a risk assessment aligned with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, helping organizations identify, prioritize, and manage cybersecurity risks effectively.
The outcome of your security or cyber threat assessment is documented in a security assessment report. This report summarizes the findings from the cyber security checklist template, including identified vulnerabilities, risk levels, and recommended mitigation strategies. The report serves as a valuable roadmap for prioritizing security improvements and communicating risks to stakeholders.
Companies will follow these 5 steps, which will be included in any cyber security checklist xls or format that you choose. Even a cyber security checklist for small business will be best served to follow the same steps as an enterprise organization, albeit with less services and personnel.
The FortifyData platform can help with the technical evaluation of a security risk assessment and performs automated and continuous cyber threat assessments of your organization giving you up to date findings on the latest vulnerabilities, threats and risks facing the attack surface of your organization, be it internal, external, cloud or third-party.
FortifyData automates a lot of the steps and processes identified in cyber security risk assessment checklists, incorporates templates and consolidates the cyber threat assessment tool capabilities into one platform. Our assessments align with, and can supplement, annual threat assessments done by your team, external teams or consultants.
The FortifyData platform incorporates NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF), NIST SP 800-53 and aligns with many other regulatory requirements for assessments, remediation and risk reporting. You will recognize their influence when it comes to assessing and analyzing the technological risks and vulnerabilities, calculating threat likelihood and risk adjustment criteria within the platform.
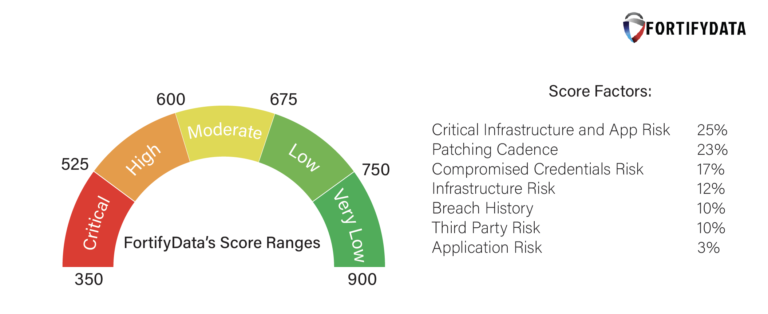
FortifyData enables clients to reflect the context of their business and cyber risk. Clients can classify identified assets by operational criticality (also allowing for identification of data types on devices) and respond to risks identified by recording the compensating control(s) in place to reduce the likelihood of threats occurring. All the findings from the cyber threat assessment are analyzed by the FortifyData cyber risk analysis AI and produced as detailed findings and summarized as a security rating that is updated on a continuous basis.
While the focus is on cyber security, physical security plays a crucial role in your overall risk assessment. Many organizations that leverage cloud services, or data centers, must consider the physical security checklist or the physical and environmental controls that the cloud, data center or colocation facility have implemented that can be inherited. Organizations in some industries still prefer to operate their own datacenters according to their risk appetite. Some industries like financial services, retail may have their own physical structures, in which case there may be something specific to the industry like a bank physical security checklist. Consider including the following physical security assessment checklist pdf criteria:
Remember, security is not just about technology. The “5 Cs of Cyber Security” framework emphasizes a holistic approach where critical operational, adminstrative and technical elements will be incorporated in the information security risk assessment pdf or solution that your company uses:
Configuration: Ensure your systems are configured securely and follow best practices.
Change Management: Implement a robust change management process to minimize the risk of introducing vulnerabilities.
Capacity Building: Train your employees on cyber security best practices and raise awareness of potential threats.
Communication: Establish clear communication protocols for reporting security incidents and sharing critical information.
Compliance: Ensure your organization complies with relevant security regulations and industry standards.
Critical components of the 5 Cs will be included in the cyber security audit checklist pdf or solution that your company might use.
An IT risk register is a centralized repository for documenting identified IT risks, their associated controls, and mitigation strategies. These can be elements that are reviewed and assessed according to an information security risk assessment pdf or solution that your company uses. Regularly updating and referencing your IT risk register ensures consistent management of your security posture. Components of a Risk Register are:
Risk Identification: The initial phase involves identifying potential risks that could impact IT operations. This includes vulnerabilities in systems, potential cyber threats, or external factors that could disrupt IT processes.
Outcome: Establishing a comprehensive understanding of the range of risks an organization may face.
Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This step helps in prioritizing risks based on their severity and the potential consequences for the organization.
Outcome: Quantifying and qualifying risks to determine where to focus mitigation efforts.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Developing and implementing strategies to mitigate or reduce the impact of identified risks. This may involve implementing security measures, contingency plans, or other proactive actions.
Outcome: Enhancing the organization’s ability to manage and minimize potential negative impacts.
Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Continuous monitoring of identified risks and regular reporting to relevant stakeholders. This ensures that the risk register remains current and aligned with the evolving IT landscape.
Outcome: Providing real-time insights into the status of risks and facilitating informed decision-making.
Proactive Risk Management: An IT Risk Register enables organizations to take a proactive approach to risk management. By identifying potential risks in advance, organizations can implement measures to mitigate or eliminate them before they escalate.
Resource Allocation: The prioritization aspect of the risk register helps organizations allocate resources efficiently. It allows them to focus on addressing the most critical and impactful risks first.
Compliance and Governance: Many industries and regulatory frameworks require organizations to adhere to specific IT security and risk management standards. Maintaining a comprehensive risk register helps demonstrate compliance and adherence to governance requirements.
Decision Support: The information provided by the IT Risk Register assists decision-makers in making informed choices about IT investments, security measures, and overall risk tolerance.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly updating the risk register ensures that it remains reflective of the current IT landscape. This iterative process allows organizations to adapt and improve their risk management strategies over time.
By implementing a structured cyber security risk assessment and utilizing a comprehensive cyber security risk assessment checklist as part of the guide for your cyber threat assessments, you can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities, prioritize risks, and allocate resources effectively. Remember, this is an ongoing process, and continuous monitoring, adaptation, and employee awareness training are crucial for maintaining a robust security posture in the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.


| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |