As you likely know, Cisco Vulnerability Management (formerly Kenna Security) is sunsetting and putting Kenna Security to end of life support.
FortifyData is more than capable as a risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) module, among its suite of cyber GRC platform offerings. FortifyData is offering remaining Kenna Security customers support for a smooth transition to FortifyData- migrating data, configure for streamlined prioritization and focus on CTEM-aligned exposure management strategies and remediation.
Key Milestone dates from the Cisco Vulnerability Management announcement
| Kenna Security Product | End of Sale Date | Last Date of Support |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Vulnerability Management (Kenna.VM) | March 10, 2026 | June 30, 2028 |
| Cisco Vulnerability Intelligence (Kenna.VI) | March 10, 2026 | June 30, 2028 |
| Cisco Vulnerability Application Security Module (AppSec) | March 10, 2026 | June 30, 2028 |
Vulnerability Management Changed
The landscape of vulnerability management has evolved significantly, driven by the exponential growth in vulnerabilities and the integration of advanced contextual factors such as Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI), Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), and operational or business context.
What was once a straightforward prioritization exercise reliant primarily on Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) scores (essentially ranking scanner outputs by severity) has transformed into a more proactive, holistic approach aligned with Continuous Threat and Exposure Management (CTEM).
This shift enables organizations to predict exploitability, incorporate real-time threat data, and weigh business impacts, turning vulnerability management from a reactive task into a strategic forefront of risk reduction.
This progression may have contributed to Cisco’s decision to sunset its Vulnerability Management platform (formerly Kenna Security) in late 2025, as the tool, while pioneering in risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM), was rooted in an earlier era that focused on aggregation and prioritization without fully addressing the demands of modern, complex environments like cloud and AI-driven systems, prompting a move toward more unified exposure management solutions.
Why FortifyData as a Kenna Security Alternative
FortifyData is a Cyber GRC platform with the capabilities that support a CTEM strategy.
Continuous asset discovery, vulnerability and threat exposure identification, threat monitoring, risk-based prioritization, remediation validation and power workflows will automate and power your CTEM strategy to manage threat exposure across assets, networks, and third parties.
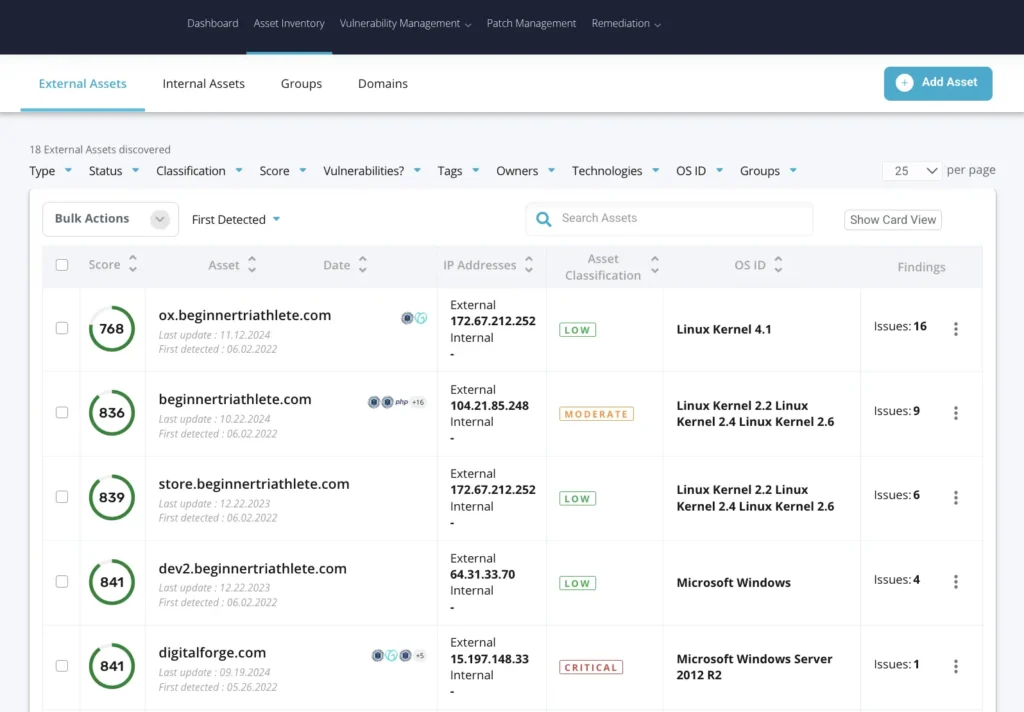
Attack Surface Management & Internal Assessments: It conducts continuous external and internal assessments and can include cloud attack surface assessments to identify and mitigate exposures that can lead to breach and attack paths that can victimize your organization.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Prioritization: This approach prioritizes vulnerabilities based on business context, incorporates threat intelligence, and exploitability, thereby focusing remediation efforts. FortifyData ingests multiple cyber threat intelligence feeds where you benefit from that enrichment against your asset inventory resulting in a dynamic and automated remediation prioritization.
Workflow for Mobilization:FortifyData’s platform for CTEM can be set to notify the relevant stakeholders when threat exposures or vulnerabilities are identified, asset footprint changes, remediation validations are confirmed or remain. The mobilization of your team based on automated findings is what moves the needle on reducing your overall threat exposure profile.
(Beyond Kenna) Third-Party Risk & Security Ratings: Vendors can be thought of as a peripheral risk, often times managed by procurement with some programs informing security as part of the process. Vendor attack surface is your attack surface in many instances. This vector should also be monitorined and considered in your cyber risk profile for prioritization. FortifyData monitors vendor extneral attack surface exposure and produces security rating scores for both internal and external stakeholders.
(Beyond Kenna) Risk & Compliance Module: FortifyData also has a risk and compliance module for managing compliance to multiple frameworks. With ASM/vulnerability findings, native in the platform, it is seamless to link them to controls, policies and evidence to evolve towards continuous compliance management.

Chief Information Officer in the Education Industry gives FortifyData Cyber Risk Management Platform 5/5 Rating in Gartner Peer Insights™ Vulnerability Assessment Market.
Read the full review here.
How Does CTEM and Vulnerability Management Differ?
The biggest difference between CTEM and traditional vulnerability management is in their approach. Traditional security waits for problems to appear, while CTEM works continuously to stay ahead of attackers.
Here’s a side-by-side look:
| Aspect | Traditional Vulnerability Management | Continuous Threat Exposure Management |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Reactive: action begins after threats or breaches occur. | Proactive: continuously identifies and prioritizes risks before they’re exploited. |
| Focus | Narrow: known threats like viruses, malware, or missing patches. | Broad:full visibility across the digital environment, including hidden and emerging risks. |
| Timing | Periodic: weekly, monthly, or quarterly scans and updates. | Continuous: always monitoring, always assessing. |
| Scope | Limited: primarily systems within the corporate network. | Comprehensive: spans cloud, endpoints, apps, vendors, and third-party ecosystems. |
| Response | Delayed: issues fixed after detection, sometimes post-damage. | Preventive: reduces exposure by closing gaps before attackers can act. |
| Tools Used | Firewalls, antivirus, and manual patching tools. | Advanced automation, threat intelligence, and unified exposure management. |
| Value to Leadership | Static reports that quickly go stale. | Dynamic insights and metrics that guide strategic decisions and resource allocation. |
Consolidated vs. Point Solution
Cybersecurity threats are escalating and legacy tools like Cisco’s Kenna Security are being phased out, platforms such as FortifyData emerge as robust alternatives by offering integrated cyber risk management that encompasses vulnerability prioritization and beyond. FortifyData provides a Kenna-like risk-based vulnerability management approach, leveraging machine learning to calculate risk scores that incorporate not just vulnerability severity but also business criticality, live threat intelligence, and exploit prediction. This enables organizations to move from reactive patching to proactive remediation, prioritizing exposures based on real-world exploitability and potential impact. By unifying these elements into a single platform, FortifyData eliminates the silos created by standalone tools, reducing the complexity and overhead of managing disparate systems.
The overarching benefits of adopting a platform that enables CTEM strategy, like FortifyData, lie in its promotion of efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced decision-making. Organizations no longer need to procure and maintain separate solutions for vulnerability scanning, threat intelligence feeds, or compliance reporting, which can lead to significant reductions in licensing fees and operational silos. Automation features, such as custom risk modeling and non-intrusive continuous assessments, streamline workflows, enabling faster risk quantification and remediation. Ultimately, this unified approach fosters a more resilient cybersecurity posture, aligning with modern demands for platform consolidation and business-contextualized risk management in dynamic digital environments.
A study from IBM and Palo Alto Networks found that companies that adopted a consolidated security platforms are achieving four times greater ROI (101%) than those with fragmented security stacks (28%).
FAQs
1. Is Kenna Security being sunset by Cisco?
Yes. Cisco Vulnerability Management (formerly Kenna Security) has an End of Sale date of March 10, 2026, and support continues until June 30, 2028. Organizations should plan migration before support fully ends.
2. What happens to existing Kenna Security users?
Existing customers can use the platform until June 30, 2028. After that, support ends. Teams must migrate data, workflows, and integrations to a new platform before the final support deadline.
3. Should teams replace Kenna with another RBVM tool or a broader platform?
Teams should evaluate long-term strategy. RBVM-only tools support prioritization, but broader CTEM-aligned platforms provide continuous monitoring, exposure management, and compliance integration for more comprehensive risk reduction.
4. What are the risks of delaying a Kenna replacement?
Delaying replacement may lead to rushed migration, outdated integrations, reduced innovation, and potential visibility gaps, increasing operational and security risk as end-of-life deadlines approach.



