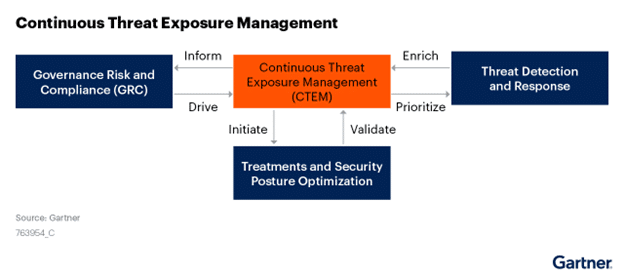
Picture this: your team races to patch a supposedly critical vulnerability on Friday afternoon, only to learn by Monday that threat actors have already shifted to a different weakness in your environment. It feels like a never-ending game of catch-up. This reactive cycle may close gaps in the moment, but it doesn’t reduce your future exposure. That’s why organizations need a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) strategy, one that constantly surfaces and prioritizes the risks most likely to impact your business.
Gartner predicted that by 2026 “organizations prioritizing their security investments based on a continuous exposure management program will be three times less likely to suffer from a breach.”
This is where CTEM becomes your asset. It is a proactive cybersecurity strategy that continuously identifies and monitors for vulnerabilities and validates which ones are exploitable.
So, who wants to reduce their breach likelihood and improve cybersecurity posture? Read on to learn everything you need in our complete CTEM guide.